
Problem Set 1
Objective
During this activity, students should be able to:
- Solve programming problems using Clojure.
This activity helps students develop the following skills, values and attitudes: ability to analyze and synthesize, capacity for identifying and solving problems, and efficient use of computer systems.
Activity Description
This activity can be developed individually or in pairs.
Solve the following programming problem set using Clojure. Place all your functions and unit tests in a file called problemset1.clj.
-
Write a function called
f2cthat takes x degrees Fahrenheit and converts them to degrees Celsius. Unit tests:(deftest test-f2c (is (= 100.0 (f2c 212.0))) (is (= 0.0 (f2c 32.0))) (is (= -40.0 (f2c -40.0))))
Tip: ºC = (ºF - 32) × 5 ÷ 9
-
Write a function called
signthat takes an integer value n. It returns -1 if n is negative, 1 if n is positive greater than zero, or 0 if n is zero. Unit tests:(deftest test-sign (is (= -1 (sign -5))) (is (= 1 (sign 10))) (is (= 0 (sign 0))))
-
The function
add-listreturns the sum of all the elements of its input list, or 0 if its empty. Assume that all the elements in the input list are numbers. Unit tests:(deftest test-add-list (is (= 0 (add-list ()))) (is (= 10 (add-list '(2 4 1 3)))) (is (= 55 (add-list '(1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10)))))
-
The function
list-of-symbols?takes a listlstas its argument. It returnstrueif all the elements (possibly zero) contained inlstare symbols, orfalseotherwise. Use thesymbol?predicate to determine if something is a symbol. Unit tests:(deftest test-list-of-symbols? (is (list-of-symbols? ())) (is (list-of-symbols? '(a))) (is (list-of-symbols? '(a b c d e))) (is (not (list-of-symbols? '(a b c d 42 e)))) (is (not (list-of-symbols? '(42 a b c)))))
-
The function
invert-pairstakes as an argument a list of vectors containing two elements each. It returns a new list with every vector pair inverted. Unit tests:(deftest test-invert-pairs (is (= () (invert-pairs ()))) (is (= '([1 a][2 a][1 b][2 b])) (invert-pairs '([a 1][a 2][b 1][b 2]))) (is (= '([1 January][2 February][3 March]) (invert-pairs '([January 1][February 2][March 3])))))
-
The function
enlistsurrounds in a list every upper-level element of the list it takes as input. Unit tests:(deftest test-enlist (is (= () (enlist ()))) (is (= '((a) (b) (c)) (enlist '(a b c)))) (is (= '(((1 2 3)) (4) ((5)) (7) (8)) (enlist '((1 2 3) 4 (5) 7 8)))))
-
The function
positivestakes a list of numberslstas its argument, and returns a new list that only contains the positive numbers oflst. Unit tests:(deftest test-positives (is (= () (positives '()))) (is (= () (positives '(-4 -1 -10 -13 -5)))) (is (= '(3 6) (positives '(-4 3 -1 -10 -13 6 -5)))) (is (= '(4 3 1 10 13 6 5) (positives '(4 3 1 10 13 6 5)))))
-
The function
dot-producttakes two arguments: the listsaandb. It returns the result of performing the dot product ofatimesb. The dot product is an algebraic operation that takes two equal-length sequences of numbers and returns a single number obtained by multiplying corresponding entries and then summing those products. Unit tests:(deftest test-dot-product (is (= 0 (dot-product () ()))) (is (= 32 (dot-product '(1 2 3) '(4 5 6)))) (is (= 21.45 (dot-product '(1.3 3.4 5.7 9.5 10.4) '(-4.5 3.0 1.5 0.9 0.0)))))
-
The function
powtakes two arguments as input: a numberaand a positive integerb. It returns the result of computingaraised to the powerb. Unit tests:(deftest test-pow (is (= 1 (pow 0 0))) (is (= 0 (pow 0 1))) (is (= 1 (pow 5 0))) (is (= 5 (pow 5 1))) (is (= 125 (pow 5 3))) (is (= 25 (pow -5 2))) (is (= -125 (pow -5 3))) (is (= 1024 (pow 2 10))) (is (= 525.21875 (pow 3.5 5))) (is (= 129746337890625 (pow 15 12))) (is (= 3909821048582988049 (pow 7 22))))
-
The function
replictakes two arguments: a listlstand an integer numbern, wheren≥ 0. It returns a new list that replicatesntimes each element contained inlst. Unit tests:(deftest test-replic (is (= () (replic 7 ()))) (is (= () (replic 0 '(a b c)))) (is (= '(a a a) (replic 3 '(a)))) (is (= '(1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4) (replic 4 '(1 2 3 4)))))
-
The function
deep-reversetakes a list as its input. It returns a list with the same elements as its input but in reverse order. If there are any nested lists, these too should be reversed. Unit tests:(deftest test-deep-reverse (is (= () (deep-reverse ()))) (is (= '(3 (d c b) a) (deep-reverse '(a (b c d) 3)))) (is (= '(((6 5) 4) 3 (2 1)) (deep-reverse '((1 2) 3 (4 (5 6)))))))
-
The function
binarytakes an integernas input (assume thatn≥ 0). Ifnis equal to zero, it returns an empty list. Ifnis greater than zero, it returns a list with a sequence of ones and zeros equivalent to the binary representation ofn. Unit tests:(deftest test-binary (is (= () (binary 0))) (is (= '(1 1 1 1 0) (binary 30))) (is (= '(1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1) (binary 45123))))
-
The function
prime-factorstakes an integernas input (assume thatn> 0), and returns a list containing the prime factors ofnin ascending order. The prime factors are the prime numbers that divide a number exactly. If you multiply all the prime factors you get the original number. Unit tests:(deftest test-prime-factors (is (= () (prime-factors 1))) (is (= '(2 3) (prime-factors 6))) (is (= '(2 2 2 2 2 3) (prime-factors 96))) (is (= '(97) (prime-factors 97))) (is (= '(2 3 3 37) (prime-factors 666))))
-
The function
packtakes a listlstas its argument. Iflstcontains consecutive repeated elements they should be placed in separate sublists. Unit tests:(deftest test-pack (is (= () (pack ()))) (is (= '((a a a a) (b) (c c) (a a) (d) (e e e e)) (pack '(a a a a b c c a a d e e e e)))) (is (= '((1) (2) (3) (4) (5)) (pack '(1 2 3 4 5)))) (is (= '((9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9)) (pack '(9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9)))))
-
The function
compresstakes a listlstas its argument. Iflstcontains consecutive repeated elements, they should be replaced with a single copy of the element. The order of the elements should not be changed. Unit tests:(deftest test-compress (is (= () (compress ()))) (is (= '(a b c d) (compress '(a b c d)))) (is (= '(a b c a d e) (compress '(a a a a b c c a a d e e e e)))) (is (= '(a) (compress '(a a a a a a a a a a)))))
-
The function
encodetakes a listlstas its argument. Consecutive duplicates of elements inlstare encoded as vectors [ne], wherenis the number of duplicates of the elemente. Unit tests:(deftest test-encode (is (= () (encode ()))) (is (= '([4 a] [1 b] [2 c] [2 a] [1 d] [4 e]) (encode '(a a a a b c c a a d e e e e)))) (is (= '([1 1] [1 2] [1 3] [1 4] [1 5]) (encode '(1 2 3 4 5)))) (is (= '([9 9]) (encode '(9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9)))))
-
The function
encode-modifiedtakes a listlstas its argument. It works the same as the previous problem, but if an element has no duplicates it is simply copied into the result list. Only elements with duplicates are converted to [ne] vectors. Unit tests:(deftest test-encode-modified (is (= () (encode-modified ()))) (is (= '([4 a] b [2 c] [2 a] d [4 e]) (encode-modified '(a a a a b c c a a d e e e e)))) (is (= '(1 2 3 4 5) (encode-modified '(1 2 3 4 5)))) (is (= '([9 9]) (encode-modified '(9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9)))))
-
The function
decodetakes as its argument an encoded listlstthat has the same structure as the resulting list from the previous problem. It returns the decoded version oflst. Unit tests:(deftest test-decode (is (= () (decode ()))) (is (= '(a a a a b c c a a d e e e e) (decode '([4 a] b [2 c] [2 a] d [4 e])))) (is (= '(1 2 3 4 5) (decode '(1 2 3 4 5)))) (is (= '(9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9) (decode '([9 9])))))
-
The function
expandtakes a listlstas its argument. It returns a list where the first element oflstappears one time, the second elements appears two times, the third element appears three times, and so on. Unit test:(deftest test-expand (is (= () (expand ()))) (is (= '(a) (expand '(a)))) (is (= '(1 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 4) (expand '(1 2 3 4)))) (is (= '(a b b c c c d d d d e e e e e) (expand '(a b c d e)))))
-
The function
gcdtakes two positive integer argumentsaandbas arguments, wherea> 0 andb> 0. It returns the greatest common divisor (GCD) ofaandb.NOTE: The GCD of two integers is the largest positive integer that divides both numbers exactly. For example, the GCD of 20 and 16 is 4.
Unit tests:
(deftest test-gcd (is (= 1 (gcd 13 7919))) (is (= 4 (gcd 20 16))) (is (= 6 (gcd 54 24))) (is (= 7 (gcd 6307 1995))) (is (= 12 (gcd 48 180))) (is (= 14 (gcd 42 56))))
-
The function
inserttakes two arguments: a numbernand a list of numberslstin ascending order. It returns a new list with the same elements aslstbut insertingnin its corresponding place. Unit tests:(deftest test-insert (is (= '(14) (insert 14 ()))) (is (= '(4 5 6 7 8) (insert 4 '(5 6 7 8)))) (is (= '(1 3 5 6 7 9 16) (insert 5 '(1 3 6 7 9 16)))) (is (= '(1 5 6 10) (insert 10 '(1 5 6)))))
-
The function
my-sorttakes an unordered list of numbers as an argument, and returns a new list with the same elements but in ascending order. You must use theinsertfunction defined in the previous exercise to write themy-sort. Do not use the predefinedsortfunction. Unit tests:(deftest test-my-sort (is (= () (my-sort ()))) (is (= '(0 1 3 3 4 6 7 8 9) (my-sort '(4 3 6 8 3 0 9 1 7)))) (is (= '(1 2 3 4 5 6) (my-sort '(1 2 3 4 5 6)))) (is (= '(1 5 5 5 5 5 5) (my-sort '(5 5 5 1 5 5 5)))))
-
The bisection method is a root-finding algorithm which works by repeatedly dividing an interval in half and then selecting the subinterval in which the root exists.
Suppose we want to solve the equation f(x) = 0. Given two points a and b such that f(a) and f(b) have opposite signs, f must have at least one root in the interval [a, b] as long as f is continuous on this interval. The bisection method divides the interval in two by computing c = (a+b) / 2. There are now two possibilities: either f(a) and f(c) have opposite signs, or f(c) and f(b) have opposite signs. The bisection algorithm is then applied to the sub-interval where the sign change occurs.
Write the function
bisection, that takesa,b, andfas arguments. It finds the corresponding root using the bisection method. The algorithm must stop when a value of c is found such that: |f(c)| < 1.0×10-15.Note:
The tests in this and the following exercise require comparing floating point numbers. In order to avoid rounding problems, we need to define the following function calledaprox=:(require '[clojure.math.numeric-tower :refer [abs]]) (defn aprox= "Checks if x is approximately equal to y. Returns true if |x - y| < epsilon, or false otherwise." [epsilon x y] (< (abs (- x y)) epsilon))
Unit tests:
(deftest test-bisection (is (aprox= 0.0001 3.0 (bisection 1 4 (fn [x] (* (- x 3) (+ x 4)))))) (is (aprox= 0.0001 -4.0 (bisection -5 0 (fn [x] (* (- x 3) (+ x 4)))))) (is (aprox= 0.0001 Math/PI (bisection 1 4 (fn [x] (Math/sin x))))) (is (aprox= 0.0001 (* 2 Math/PI) (bisection 5 10 (fn [x] (Math/sin x))))) (is (aprox= 0.0001 1.618033988749895 (bisection 1 2 (fn [x] (- (* x x) x 1))))) (is (aprox= 0.0001 -0.6180339887498948 (bisection -10 1 (fn [x] (- (* x x) x 1))))))
-
The derivate of a function f(x) with respect to variable x is defined as:
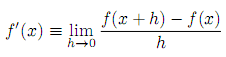
Where f must be a continuous function. Write the function
derivthat takesfandhas its arguments, and returns a new function that takesxas argument, and which represents the derivate offgiven a certain value forh.The unit tests verify the following derivates:
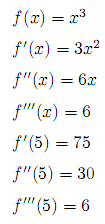
Unit tests:
(defn f [x] (* x x x)) (def df (deriv f 0.001)) (def ddf (deriv df 0.001)) (def dddf (deriv ddf 0.001)) (deftest test-deriv (is (aprox= 0.05 75 (df 5))) (is (aprox= 0.05 30 (ddf 5))) (is (aprox= 0.05 6 (dddf 5))))
-
Simpson's rule is a method for numeric integration:
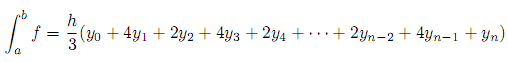
Where n is an even positive integer (if you increment the value of n you get a better approximation), and h and yk are defined as follows:
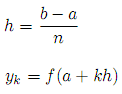
Write the function
integral, that takes as argumentsa,b,n, andf. It returns the value of the integral, using Simpson's rule. The unit tests verify the following single and double integrals (withn= 10):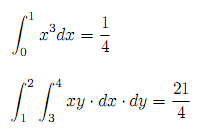
Unit tests:
(deftest test-integral (is (= 1/4 (integral 0 1 10 (fn [x] (* x x x))))) (is (= 21/4 (integral 1 2 10 (fn [x] (integral 3 4 10 (fn [y] (* x y))))))))
Deliverables
The program source file must include at the top the authors’ personal information (name and student id) within comments. For example:
;---------------------------------------------------------- ; Activity: Problem Set 1 ; Date: September 19, 2018. ; Authors: ; A01166611 Pepper Pots ; A01160611 Anthony Stark ;----------------------------------------------------------
Also, each function should include a documentation string (docstring) with a brief description of its behavior. For example:
(defn max2 "Returns the largest of the two numbers x and y." [x y] (if (> x y) x y))
Instrucciones para subir archivo
Para entregar el archivo problemset1.clj, ingresa los siguientes datos:
Only one team member needs to upload the file.
Due date is Wednesday, September 19.
Evaluation
This activity will be evaluated using the following criteria:
| -10 | The program doesn't contain within comments the author's personal information. |
|---|---|
| -30 | A docstring is missing in one or more functions. |
| 10 | The program contains syntax errors. |
| 1 | The program was plagiarized in whole or in part. |
| 10-100 | Depending on the amount of exercises that were solved correctly. |